Medicaid is a vital government-funded health insurance program that plays a crucial role in providing affordable healthcare to millions of low-income individuals and families across the United States. Whether you’re considering applying for Medicaid, need help understanding its benefits, or want to know how it differs from other health insurance programs, this article will provide an in-depth look at what Medicaid is, who qualifies, and how it can benefit you.
What is Medicaid?
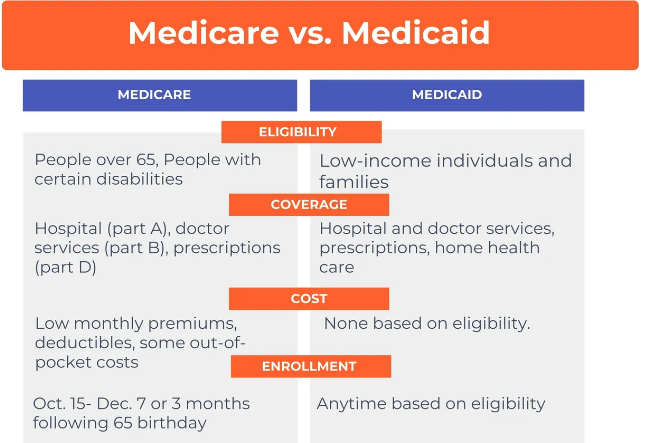
Medicaid is a state and federally funded program that provides healthcare coverage to eligible low-income individuals, families, seniors, and people with disabilities. Established in 1965 under the Social Security Act, Medicaid is jointly administered by the federal government and individual state governments. While the program is federally funded, each state has its own guidelines and rules for eligibility, enrollment, and benefits. As a result, Medicaid programs may vary from state to state in terms of coverage options, eligibility requirements, and benefits offered.
Medicaid is one of the largest providers of health insurance in the U.S., covering more than 70 million Americans as of recent data. It provides access to essential health services like doctor visits, hospital care, prescription medications, and preventive services. Medicaid is especially important for vulnerable populations, such as low-income children, pregnant women, elderly individuals, and people with disabilities, helping them get the care they need regardless of their ability to pay.
Who Qualifies for Medicaid?
Eligibility for Medicaid is primarily determined by income and household size, though other factors like age, disability, pregnancy status, and employment may also influence eligibility. Medicaid is designed to serve the most vulnerable populations who cannot afford health insurance on their own. While specific eligibility requirements vary by state, the following groups are generally eligible for Medicaid:
Low-Income Adults: Many low-income adults who do not have children qualify for Medicaid, especially if their income is at or below the federal poverty level (FPL). In states that expanded Medicaid under the Affordable Care Act (ACA), more adults became eligible for coverage.
Children: Medicaid offers coverage to low-income children in all states. Many children qualify for the program, regardless of their parents’ income level, as long as the family meets certain criteria.
Pregnant Women: Pregnant women who meet income and other eligibility requirements can receive Medicaid coverage for the duration of their pregnancy and, in some states, for a period after the child is born.
Seniors: Medicaid covers low-income individuals who are 65 years or older. These individuals may also be eligible for Medicaid to help pay for long-term care, such as nursing home care, that is not typically covered by Medicare.
Individuals with Disabilities: People with disabilities, both physical and mental, can qualify for Medicaid, regardless of their age, if they meet the income and disability criteria.
Families with Dependent Children: Families who are caring for dependent children, and whose income is below a certain threshold, can qualify for Medicaid. In some states, coverage for children may be extended up to a higher income level.
Other Groups: Some states also provide coverage for additional groups, such as former foster care youth or individuals who are HIV-positive.
It’s important to note that Medicaid eligibility varies depending on the state in which you live. Some states have expanded Medicaid under the ACA, allowing more low-income adults to qualify, while others have not. To learn about the specific Medicaid eligibility requirements in your state, visit your state’s Medicaid website or speak to a Medicaid representative.
How Does Medicaid Work?
Medicaid functions as a health insurance program that covers a broad range of medical services, though the specific benefits and services provided may vary by state. In general, Medicaid covers the following essential services:
Inpatient and Outpatient Hospital Services: Medicaid provides coverage for hospital stays, surgeries, and outpatient procedures.
Physician Services: Medicaid covers visits to primary care doctors, specialists, and other medical providers.
Prescription Medications: Medicaid helps cover the cost of prescription drugs, although some states may have limitations on certain medications.
Preventive Services: Medicaid covers a variety of preventive services, such as vaccinations, screenings, and wellness visits, to help prevent serious health issues from developing.
Mental Health Services: Medicaid covers mental health services, including counseling, therapy, and substance abuse treatment, which is critical for individuals with mental health conditions.
Emergency Services: Emergency room visits and ambulance transportation are covered by Medicaid for eligible individuals.
Long-Term Care Services: Medicaid is often used to pay for long-term care needs such as nursing home stays or home health care services, which are not typically covered by Medicare.
Dental and Vision Care: While Medicaid may offer limited dental and vision coverage, these services can vary significantly depending on the state. Some states provide comprehensive dental and vision benefits, while others may only cover basic services.
Maternity and Newborn Care: Medicaid covers maternity care and services related to childbirth, as well as newborn care for infants.
Home and Community-Based Services (HCBS): Many states offer services that allow individuals to receive care in their homes or communities instead of institutional settings, such as nursing homes.
Medicaid may also cover additional services, including transportation to medical appointments, medical equipment, and hospice care, depending on the state’s program.
How Medicaid Can Benefit You
Medicaid offers a range of benefits that can significantly improve your access to healthcare, particularly if you face financial hardships or have complex medical needs. Here are some of the key ways Medicaid can benefit you:
- Access to Affordable Healthcare
For many individuals and families, the primary benefit of Medicaid is the ability to receive healthcare services that they might otherwise be unable to afford. Without Medicaid, many low-income individuals would go without necessary medical care, leading to worsened health outcomes and higher healthcare costs in the future. Medicaid ensures that financial barriers don’t prevent you from receiving essential medical treatment, including emergency care, surgery, doctor’s visits, and prescription medications. - Comprehensive Coverage
Medicaid provides a broad range of healthcare services, including preventative care, mental health services, and long-term care, which are essential for maintaining a healthy life. Medicaid’s comprehensive coverage helps reduce out-of-pocket medical expenses, which could otherwise be overwhelming for families with limited financial resources. - Coverage for Chronic Conditions and Disabilities
Medicaid is crucial for individuals with chronic conditions or disabilities who require ongoing medical care and services. This includes coverage for long-term care in nursing homes or home health care, as well as treatments for conditions like diabetes, heart disease, or mental health disorders. Medicaid ensures that individuals with disabilities or chronic illnesses have access to necessary services that improve their quality of life. - Family and Maternal Health
Medicaid’s coverage for children and pregnant women helps ensure that families have access to prenatal care, delivery services, and pediatric care. This is vital for reducing infant mortality rates, improving maternal health, and preventing chronic health problems in children. By providing coverage to expectant mothers and young children, Medicaid helps reduce health disparities and promotes healthier outcomes for families. - Mental Health and Substance Use Disorder Coverage
Mental health services and addiction treatment are often expensive and inaccessible for those without insurance. Medicaid offers coverage for mental health counseling, therapy, and substance abuse treatment, which are essential for individuals struggling with mental health issues or addiction. - Long-Term Care Services
For elderly individuals or those with disabilities who require long-term care, Medicaid plays a critical role in providing nursing home care or home health services. These services can be financially out of reach for many people, and Medicaid ensures that they have access to the care they need.
How to Apply for Medicaid
To apply for Medicaid, you need to meet the eligibility requirements in your state. The application process typically involves providing personal information, such as income, household size, and residency status. You can apply online, by mail, or in person at your local Medicaid office. Many states also offer a streamlined application process through healthcare.gov or state-specific marketplaces, where you can apply for both Medicaid and other insurance options.
If you are approved for Medicaid, you will receive a Medicaid card that you can use to access covered healthcare services.
Conclusion
Medicaid is an essential health insurance program that provides millions of low-income individuals, families, seniors, and people with disabilities with access to affordable and comprehensive healthcare services. By covering a wide range of medical needs, including preventive care, doctor visits, prescription medications, and long-term care, Medicaid helps ensure that financial barriers do not prevent you from receiving the care you need.
If you think you may be eligible for Medicaid, it’s important to explore your options and apply through your state’s Medicaid program. Medicaid can provide you with the healthcare coverage you need to protect your health and well-being, especially in times of financial hardship or when facing significant medical challenges.